LEFT, RIGHT, LEN & FIND - Useful Spreadsheets Functions
This article explores fundamental string functions of LEN, LEFT, RIGHT, & FIND and their practical applications.
The LEN Function
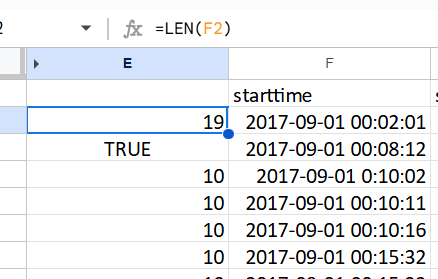
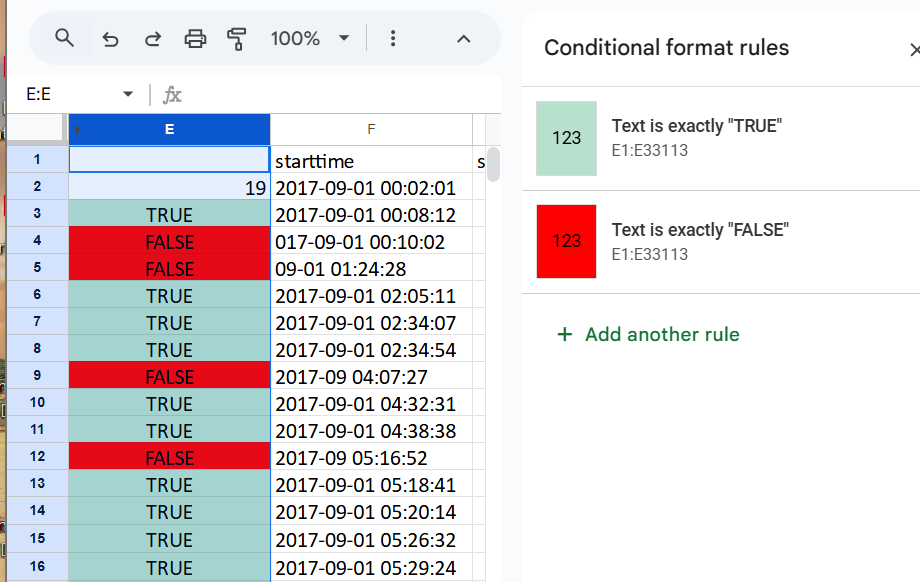
The LEN function calculates the length of a text string by counting all characters, including spaces. In my example, I applied the LEN function to a datetime string F2, to first identify the number of characters contained in the column cells. Then I used that identified number of characters “19” to then easily check if all the remaining cells contain the same numbers of characters using =LEN(F2)=19 which would return TRUE or FALSE. Lastly, I added conditional formatting for additional ease in data validation.
2017-09-01 00:02:01 (19 total characters)
The LEFT Function: Extracting From The Beginning
The LEFT function lets you extract a specified number of characters from the beginning of a string. This is particularly useful when working with formatted data like dates and times.
A common application is extracting the date portion from a datetime string by taking the first 10 characters.
2025-11-23 (10 characters total)
The RIGHT Function: Extracting From The End
Similarly, the RIGHT function extracts characters from the end of a string. In my example I have the datetime string formatted as date first followed by the time. This function can be used to isolate the time component that is on the right of the string. In my example I would like to select all the numbers and the colons as well.
2025-11-23 00:23:32 (8 characters total)
The FIND Function: Locating Characters
The FIND function is used for locating specific characters or substrings within a text string. It returns the position number where the specified character or substring begins.
In my example I use the FIND function to locate a space in a datetime string:
Enter =FIND(" ", D2) where the space is the character I am searching for.
For example, in a datetime string like "2025-11-23 00:23:32", FIND would return 11, indicating the space is the 11th character.
The key points about FIND:
Returns the numeric position of the searched character/substring
Is case-sensitive for accurate matching
Particularly useful for parsing structured strings like dates and times
Practical Applications
String function real use case scenarios:
Data Cleaning and Standardization
Using LEN to verify phone number has exactly 10 digits:
Phone number: 9876543210
=LEN(A2) = 10 // Returns TRUE if phone number has exactly 10 digits
Separating Combined Data
Breaking down a full name into first and last names using RIGHT, LEFT, & FIND:
Full Name: "John Smith"
First Name: =LEFT(A2, FIND(" ", A2)-1) // Returns "John"
Last Name: =RIGHT(A2, LEN(A2)-FIND(" ", A2)) // Returns "Smith"
Validating Date Format
Checking if dates follow YYYY-MM-DD format using AND,LEN, & MID:
Date: 2025-11-23
=AND(LEN(A2)=10, MID(A2,5,1)="-", MID(A2,8,1)="-") // Returns TRUE if format is correct
Extracting Specific Portions
Getting specific parts from an email address using LEFT,RIGHT, LEN, & FIND:
Email: A2 = "user.name@company.com"
Username: =LEFT(A2, FIND("@", A2)-1) // Returns "user.name"
Domain: =RIGHT(A2, LEN(A2)-FIND("@", A2)) // Returns "company.com"
Key Takeaways
Fundamental for data analysis when string length validation and character extraction is needed.
LEN function calculates the length of a text string by counting all characters, including spaces.
LEFT - lets you extract a specified number of characters from the beginning of a string.
RIGHT - lets extracts a specified number characters from the end of a string.
FIND is case-sensitive, returns the numeric position of the searched character/substring & is useful for parsing dates and times
Hello! I'm Miguel, and I'm documenting my journey in data analytics. I welcome any feedback, freelance, and collaboration opportunities.
Connect with me: